Geysers Are Formed When Groundwater Is Heated by Nearby Magma
Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. Its powerful jet of steam ejects the column of water above it.
Geysers are in fact formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma.
. Geysers are made from a tube. Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. Generally geysers require that large amounts of groundwater fill underground cavities in an area of volcanic activity.
They think that large amounts of groundwater fill underground cavities. Each geyser has unique characteristics due to complex internal plumbing. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma molten rock or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earths crust.
By soetrust December 21 2021. 3 on a question Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. The water in these deep cavities is heated by nearby magma.
Generally geysers require that large amounts of groundwater fill underground cavities in an area of volcanic activity. When it reaches the surface features such as geysers fumaroles hot springs and mud pits are created. The water in these is heated by nearby magma.
True Or False THIS IS THE BEST ANSWER the real answer is kjdckjdc Related PostsThe opening through which magma flows through. Geysers Are Formed When Groundwater Is Heated By Nearby Magma. The tube is filled with water.
How do hot springs and geysers form. This 13 words question was answered by Jared M. The tube is filled with water.
Hot springs and geysers also are manifestations of volcanic activity. True Or False - Soetrust. Geysers result from the heating of groundwater by shallow bodies of magma.
The spouting action is caused by the sudden release of pressure that has been confining near-boiling water in deep narrow conduits beneath a geyser. Geysers result from the heating of groundwater by shallow bodies of magma. Geysers are the most well known geothermal feature.
The total heat flux from these thermal features is estimated. Geysers are made from a tube-like hole in the Earths surface that runs deep into the crust. Suddenly some of the water flashes into steam and expands rapidly.
Amazon Luna launches with freebies for Prime subscribersAmazon Luna special offer for Prime membersTry Amazon Luna Now. Suddenly some of the water flashes into steam and expands rapidly. Geysers are made from a tube-like hole in the Earths surface that runs deep into the crust.
Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. They can also be formed by volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occasionally as well. Near the bottom of the tube is molten rock called magma which heats the water in the tube.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE. Correct answer to the question Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. When groundwater heated by magma rises to the surface and collects in a natural pool it is called a.
Near the bottom of the tube is molten rock called magma which heats the water in the tube. Yellowstone National Park in the United States is one of the most famous areas of hot springs and geysers in the world. They are generally associated with areas that have seen past volcanic activity.
As steam or gas bubbles begin to form in the conduit hot water spills from the vent of the geyser and the pressure is lowered on. Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. Geysers erupt because the water is trapped.
The heat from the magma causes water to become steam. How is geyser formed. Geysers are in fact formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma.
Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. The question contains content related to Biology and Science. On StudySoup on 5312017.
The spouting action is caused by the sudden release of pressure that has been confining near-boiling water in deep narrow conduits beneath a geyser. They can also be formed by volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occasionally as well. They are generally associated with areas that have seen past volcanic activity.
Hot springs - Groundwater heated by a nearby body of magma rises to the surface and collects in a natural pool. Since its upload it. When magma heats groundwater it may come to the surface as a hot spring or a geyser.
THIS USER ASKED Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma. The cause of volcanic activity. Geysers are formed when groundwater is heated by nearby magma.
What landform is created when magma squeezes between rock layers to form a hardened slab of rock. They are generally associated with areas that have seen past volcanic activity. Scientists do not completely understand how geysers work.
The water in these deep cavities is heated by nearby magma. Geysers result from the heating of groundwater by shallow bodies of magma. They result from the interaction of groundwater with magma or with solidified but still-hot igneous rocks at shallow depths.
Why do geysers erupt rather than bubble to the surface like a hot spring. A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma. Water in the lower part of the tube close to the magma becomes superhot.
How Close Is Magma To The Surface In Yellowstone Quora

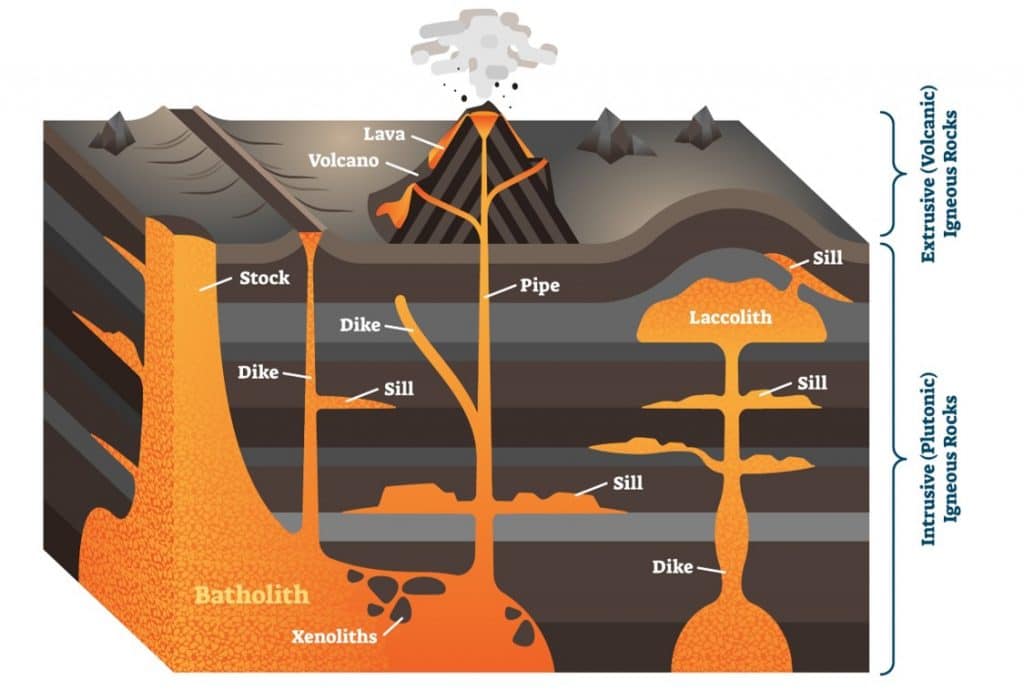
Section 4 Volcanic Landforms Nitty Gritty Science
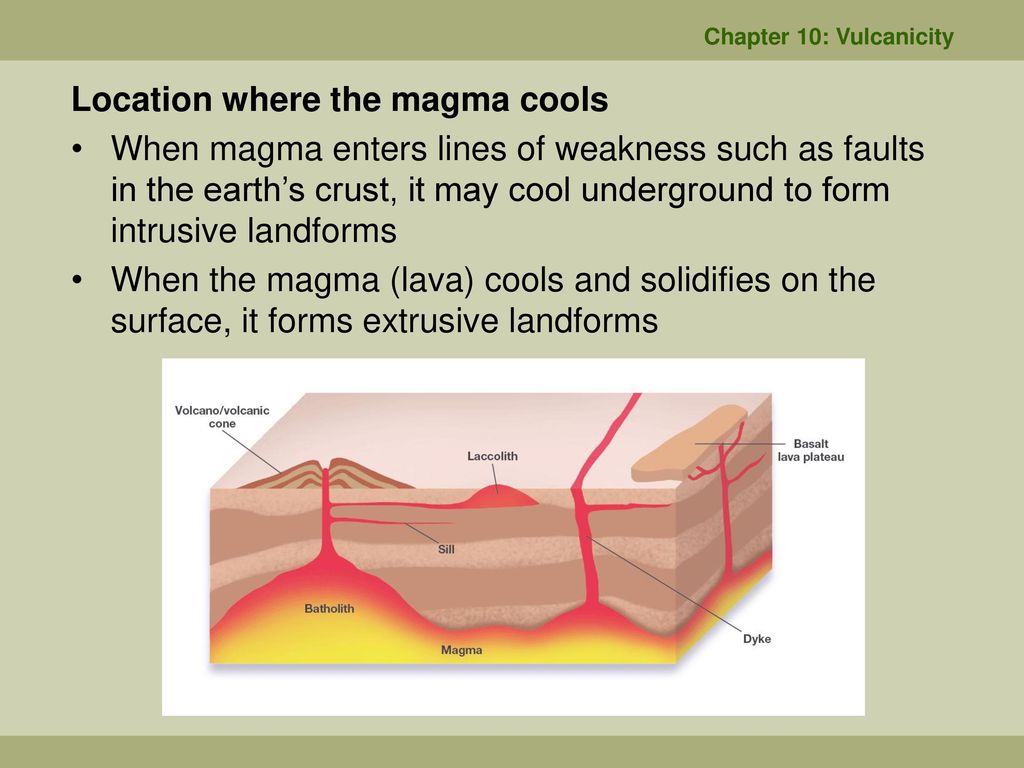
Chapter 10 Vulcanicity Ppt Download
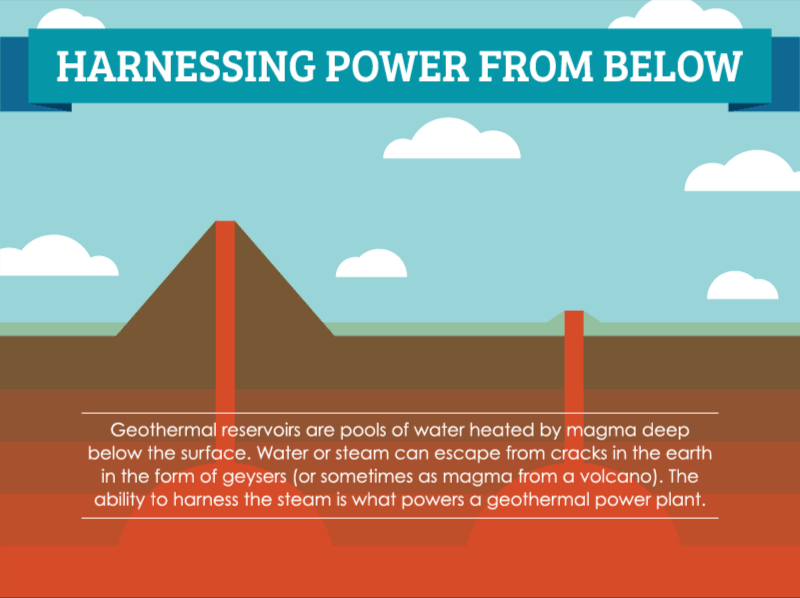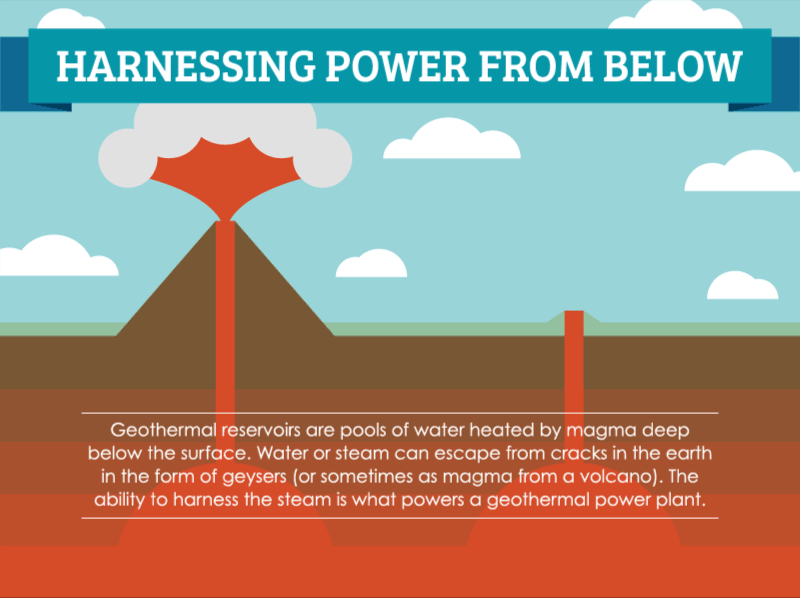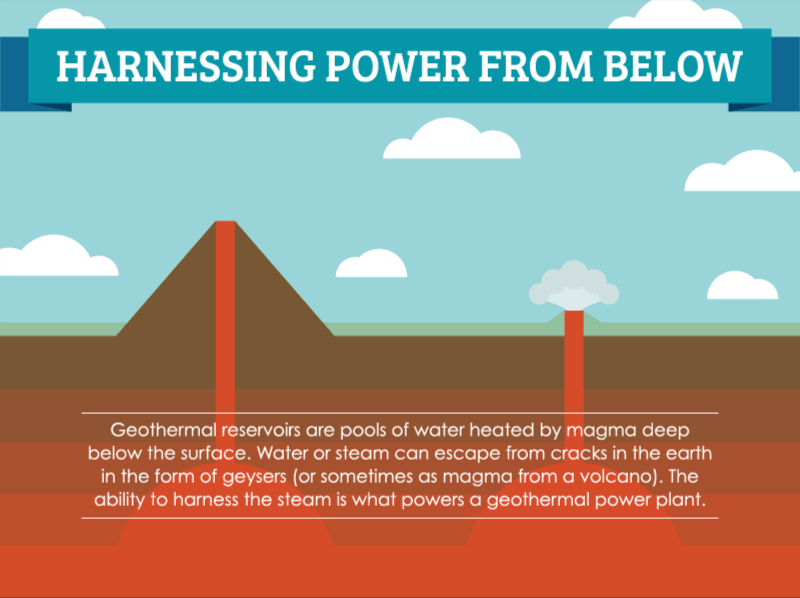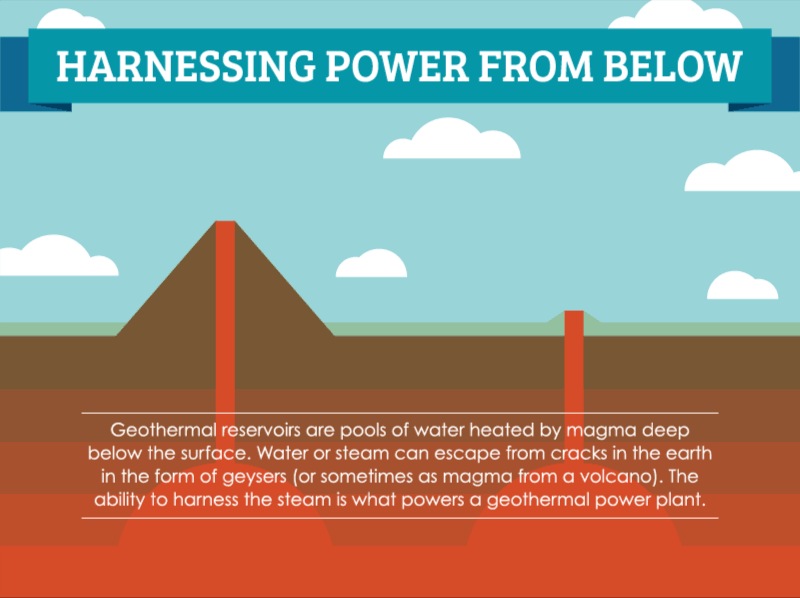
How Geothermal Energy Works Saveonenergy Com
Which Type Of Rock Is Critical For The Formation Of Geysers Quora

Geyser Definition Formation Locations Facts Britannica

Groundwater Water That Soaks Into The Ground After Rain Ppt Download

Geyser Definition Formation Locations Facts Britannica

Crystal Cave In Naica Chihuahua Mexico Crystal Cave Giant Crystal Natural Wonders
Do All Volcanoes Erupt The Same Way Quora
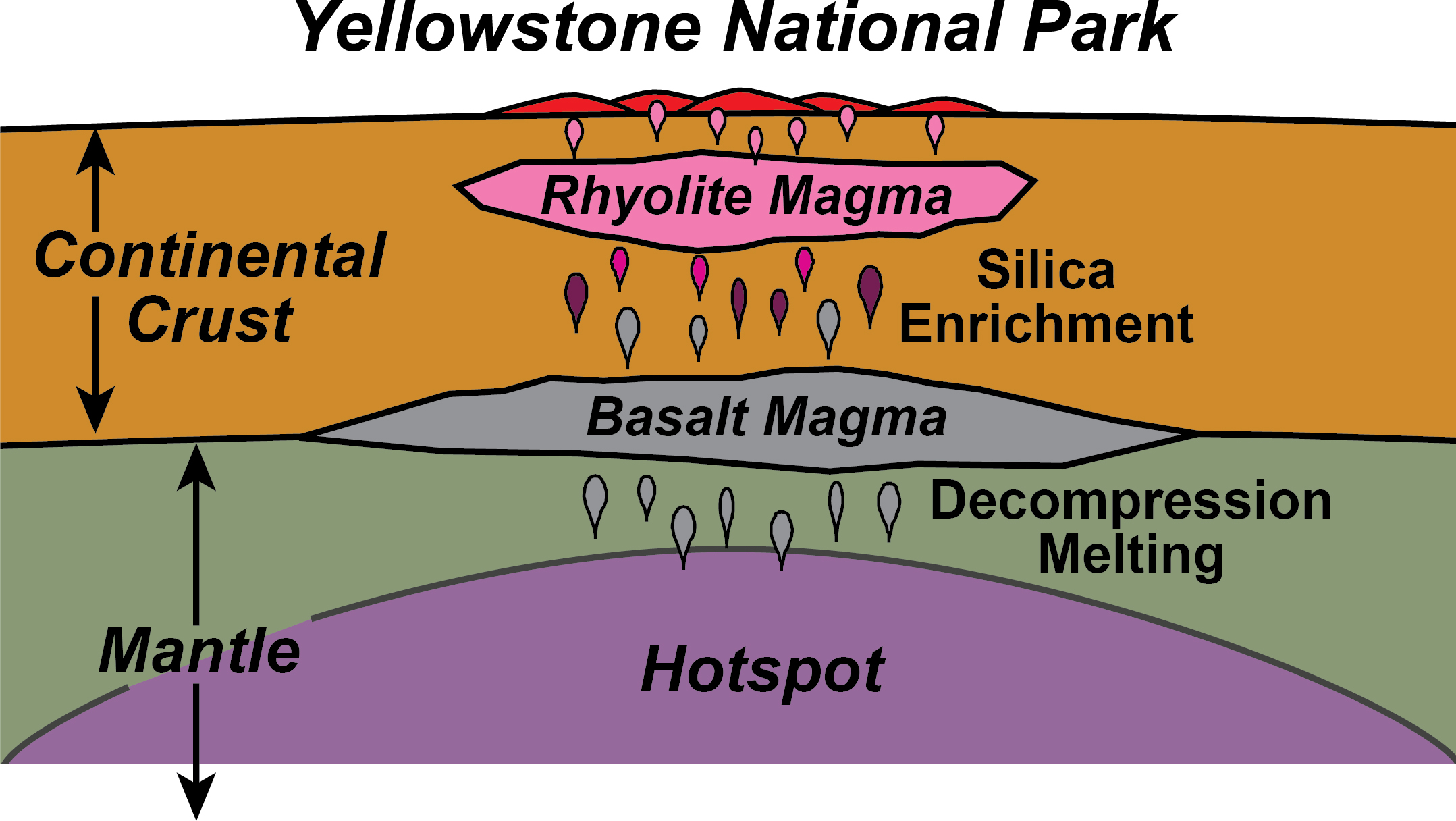
Continental Hotspot Geology U S National Park Service

Volcanic Processes Water Water Can Be Heated By Magma Or Lava Process Of Heating Water Can Create Geysers Hot Springs Fumaroles Mud Pots Heated Ppt Download

Geothermal Energy Mink Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library

Geyser Definition Formation Locations Facts Britannica

Geothermal Systems In High Enthalpy Regions Springerlink

Geyser An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


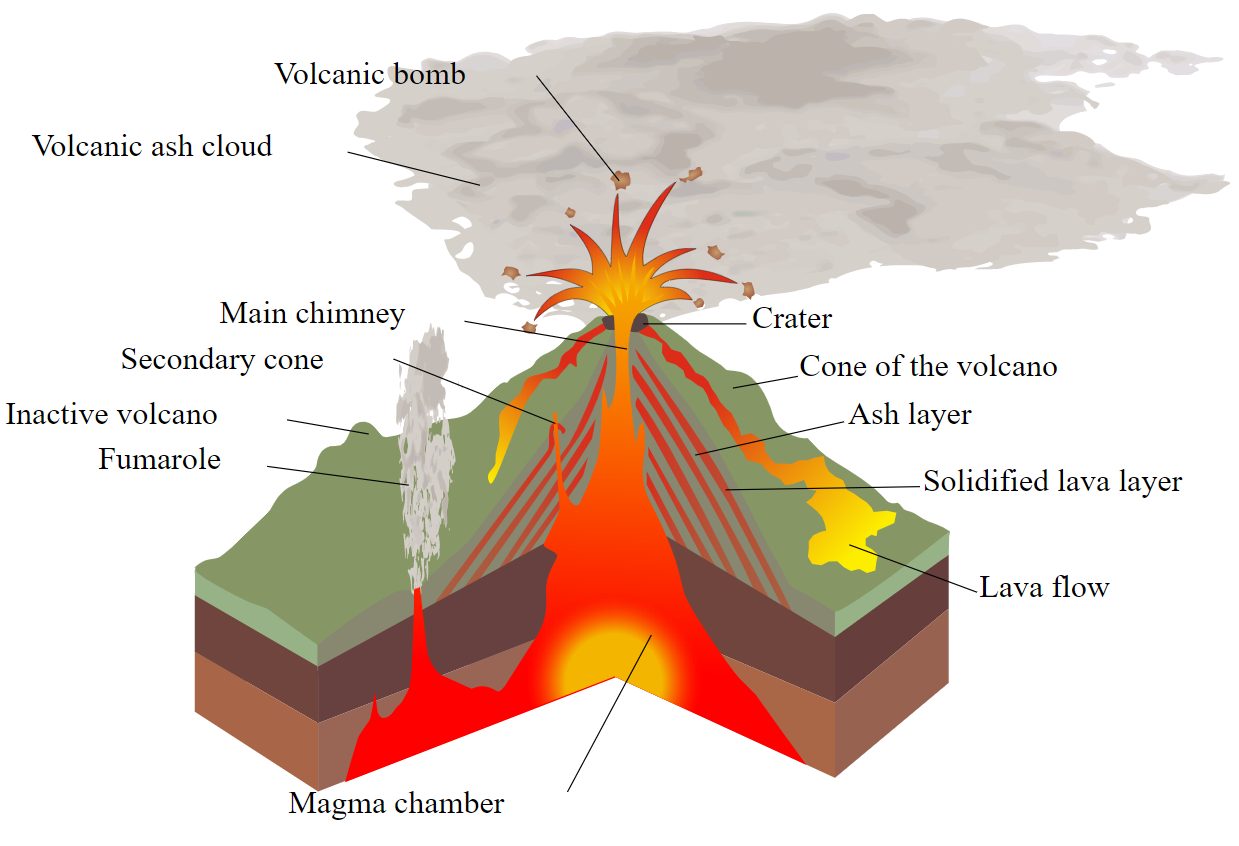
Comments
Post a Comment